Wuhan City in China was the first place to report COVID-19 in the world and—between December 2019 and May 2020—caused nearly two-thirds of all COVID-19 cases in China. Now, researchers reporting in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases have tested more than 60,000 healthy individuals in China for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and concluded that thousands of Wuhan residents were infected with asymptomatic cases of COVID-19 after the infection was believed to be under control in China.
Rapid antibody tests are used to diagnosis present and past infections with the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19; positive IgG antibodies suggests a previous infection while IgM antibodies mean a current or recent infection. Detection of both types of antibodies can give a better understanding of the number of asymptomatic infections in a population over time. In Wuhan, the number of COVID-19 cases peaked in February 2020 and the city was initially declared to be free of disease in late April, although small clusters of cases appeared in later months.
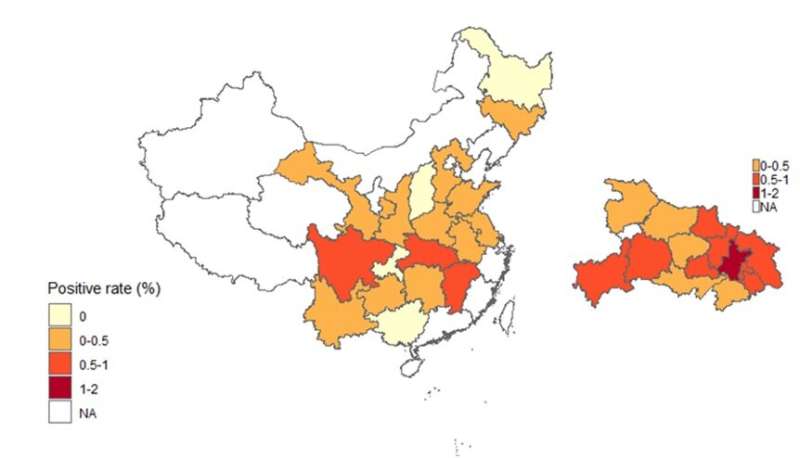
In the new work, Xue-jie Yu of Wuhan University, China, and colleagues studied the prevalence of IgG and IgM antibodies in blood samples collected between March 6 and May 3, 2020, from 63,107 individuals in China. All people tested were healthy and were undergoing screening before returning to work.
Consistent with a large number of cases having occurred in Wuhan, the percentage of people with positive SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, about 1.68%, was significantly higher than in other regions of China, where antibody positivity averaged 0.38%. Moreover, according to the IgM positive rate of 0.46% in Wuhan, the researchers estimated that thousands of people in Wuhan were infected asymptomatically between March and May 2020, when there were not clinically reported cases of COVID-19.
Source: Read Full Article
