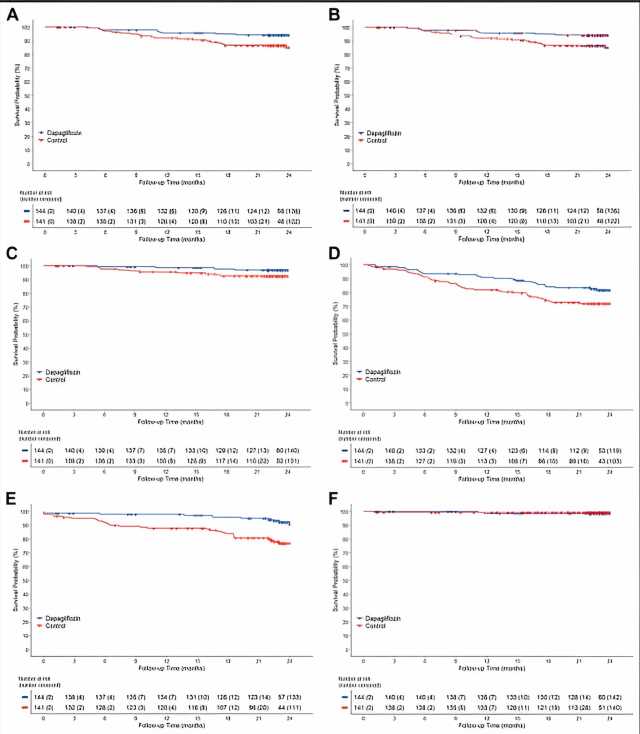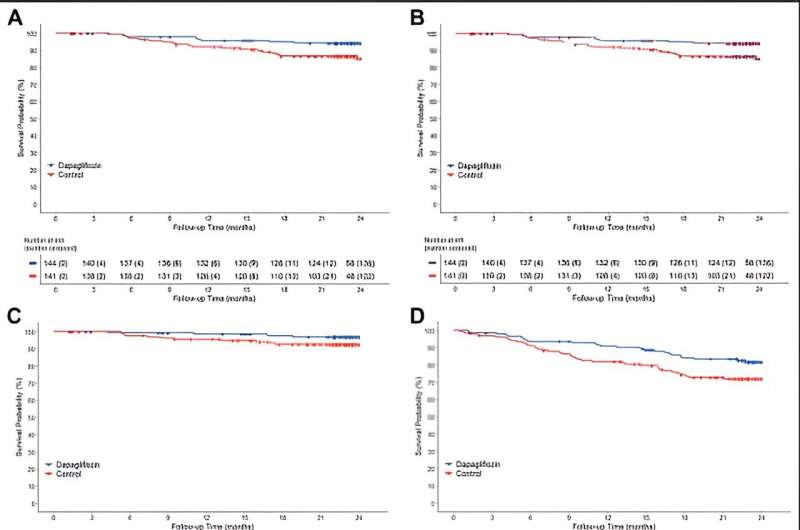
The DAPPER study was conducted with the National Cardiovascular Center as the principal investigator, with 294 patients participating from 18 facilities in Japan. In this study, researchers investigated whether dapagliflozin suppresses urinary albumin excretion, a sensitive marker of kidney damage, and whether it also suppresses cardiovascular events in patients with chronic heart failure and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
This study was conducted as a multicenter, randomized, open-label, standard-treatment control, parallel-group comparison with two years of follow-up. The recommended dose of dapagliflozin for heart failure is 10 mg. However, in this study, dapagliflozin was administered at either 5 mg or 10 mg.
The results showed that 87.7% of patients in the dapagliflozin group received 5 mg at the end of the 2-year observation period. Although dapagliflozin did not reduce urinary albumin excretion, the primary endpoint, the secondary endpoint of cardiovascular events (cardiovascular death or hospitalization for cardiovascular events and additional heart failure medication) was reduced in the dapagliflozin group compared to the standard treatment group.
This is the first report that dapagliflozin administration centered on 5 mg suppressed cardiovascular events in patients with chronic heart failure and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The results of this study are expected to provide valuable insight into treatment strategies for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic heart failure. They are expected to make a significant contribution to clinical practice.
The work is published in the journal eClinicalMedicine.
More information:
Fumiki Yoshihara et al, DAPagliflozin for the attenuation of albuminuria in Patients with hEaRt failure and type 2 diabetes (DAPPER study): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, parallel-group, standard treatment-controlled trial, eClinicalMedicine (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102334
Journal information:
EClinicalMedicine
Source: Read Full Article