The importance of accurate prenatal diagnosis in preventing birth abnormalities cannot be overstated. Traditional karyotyping (a test to examine chromosomes in a sample of cells) dates back to the late 1960s and is well-established, but advancements in technology offer new options.
A new study led by Dr. Sun Yan, Dr. Lijie Song, Dr. Xueqin Guo at BGI Genomics R&D Division and published on Journal of Medical Genetics sought to validate Low-Pass Genome Sequencing (LP GS) as an alternative to Chromosomal Microarray Analysis (CMA) for prenatal diagnosis. Additionally, it explored the critical factor of sequencing depth in LP GS, which has been a gap in previous research.
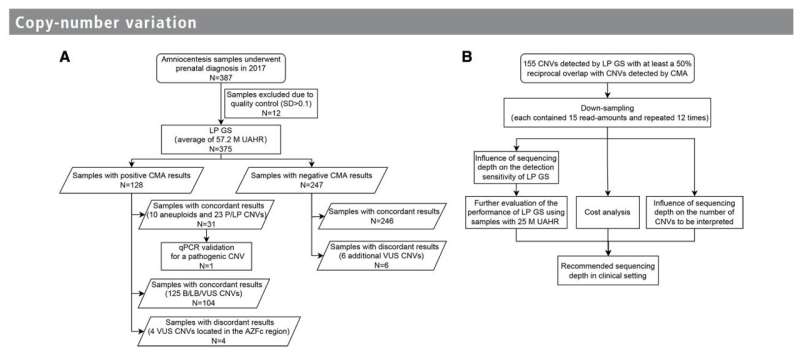
The study analyzed 375 amniotic fluid samples and compared the diagnostic performance of LP GS to CMA. Surprisingly, both methods achieved the same diagnostic yield of 8.3%. In cases with negative CMA results, LP GS outperformed by revealing six additional Copy Number Variations (CNVs—Genomic alterations that result in an abnormal number of copies of one or more genes.) of uncertain significance.
This result emphasizes the robustness of LP GS in detecting genetic abnormalities, potentially missed by CMA.
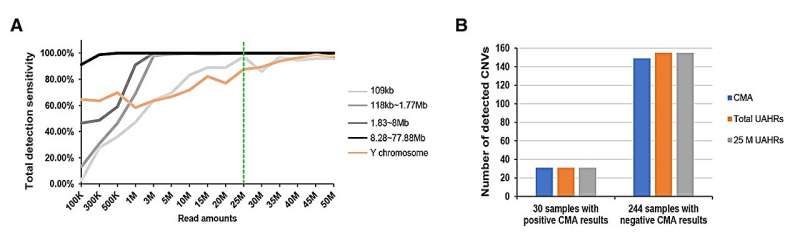
The study found out that the size of CNVs significantly impacted Low-Pass Genome Sequencing detection sensitivity. Small CNVs and those situated in specific regions, like the azoospermia factor c (AZFc) region of the Y chromosome, were more sensitive to variations in sequencing depth. In contrast, larger CNVs were less affected by sequencing depth.
The research recommended a sequencing depth of 25 million Uniquely Aligned High-Quality Reads (UAHRs) as optimal for detecting most aneuploidies and microdeletions/microduplications. This sequencing depth strikes a balance between detection sensitivity, cost-effectiveness, and interpretation workload.
These findings add crucial validation and data regarding LP GS as a first-tier prenatal diagnostic method in real clinical settings, highlighting its pivotal role of sequencing depth in LP GS and establishes the 25 million UAHRs threshold.
Enabling better decisions, reducing genetic abnormalities risks
Prenatal diagnosis is instrumental in preventing birth defects due to chromosomal abnormalities. This research findings reveal that LP GS can be a robust and cost-effective alternative to CMA in prenatal screening. It not only matches CMA’s performance but offers a vital advantage in detecting additional CNVs. This enhanced capability can improve clinical decision-making and reduce risks associated with undetected genetic abnormalities, ultimately promoting safer pregnancies.
These findings provide a significant leap forward in prenatal care. The ability to accurately detect aneuploidies and microdeletions/microduplications enable reducing birth defects, more accurate patient care and better clinical decision-making.
More information:
Yeqing Qian et al, Validation and depth evaluation of low-pass genome sequencing in prenatal diagnosis using 387 amniotic fluid samples, Journal of Medical Genetics (2023). DOI: 10.1136/jmg-2022-109112
Journal information:
Journal of Medical Genetics
Source: Read Full Article
