Cardiac pacemakers are battery-dependent, where the pacing leads are prone to introduce valve damage and infection. In addition, complete pacemaker retrieval is necessary for battery replacement. Despite the presence of a wireless bioelectronics device to pace the epicardium, surgeons still need to implant the device via thoracotomy, an invasive surgical procedure in health care that necessitates wound healing.
Shaolei Wang and a research team of scientists in bioengineering, microbiology, and cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, devised a biocompatible wireless microelectronics device to form a microtubular pacemaker for intravascular implantation and pacing. Their wok has been published in Science Advances.
The pacemaker provided effective pacing to restore cardiac contraction from a non-beating heart in a porcine animal model. The microtubular pacemaker paves the way for the minimally-invasive implantation of leadless and battery-free microelectronics for health care and cardiac pace restoration.
Advances in vascular surgery
Microstimulators can be implanted as cardiac, gastric, neural, and urological devices to sustain life. While pacing leads are prone to discharge, fracture and biofilm formation, the effort to generate leadless pacemakers that are battery-free for minimally invasive implantation remain an unmet challenge in biomedical engineering.
Advances in catheter-based deployment for biomedical implants include bioprosthetic valves. In this work, Wang and colleagues established a self-assembled, implantable, microtubular pacemaker made of lightweight and wireless constituents, to provide high electrical output and operational capacity to facilitate intravascular myocardial pacing and mechanical coupling.
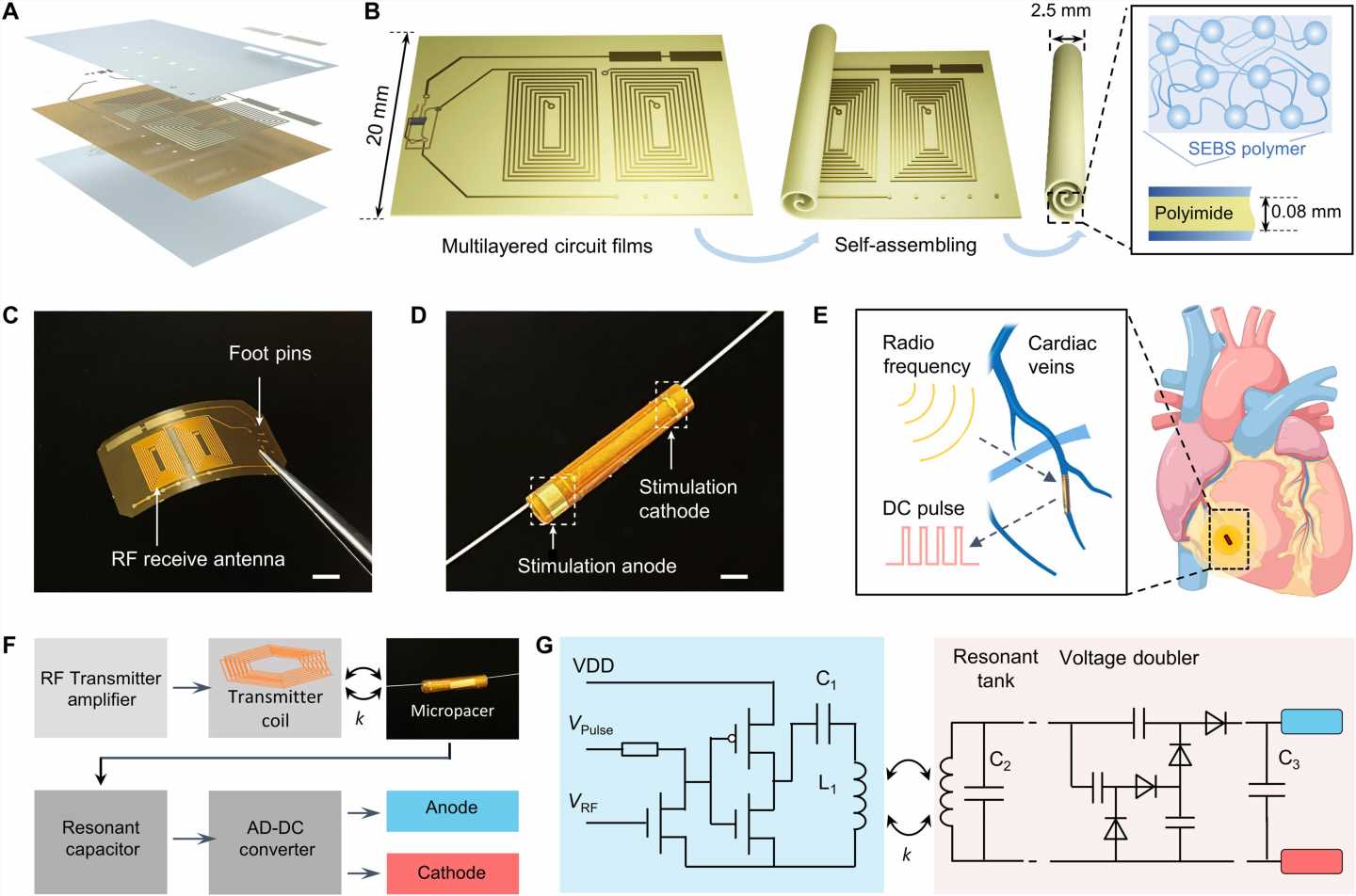
Forming a self-assembled, microtubular pacemaker
The team accomplished this by designing a microtubular pacemaker to reduce the mechanical burden of pacing-related medical complications. They generated a wireless radiofrequency module in a thin, flexible polyimide membrane to receive power transfer from the external transmitter. They encapsulated the polyimide membrane with an elastomer layer to insulate the circuits and optimized power transfer efficiency to the microtubular pacemaker by designing a radiofrequency power transmitter for electrical stimulation.
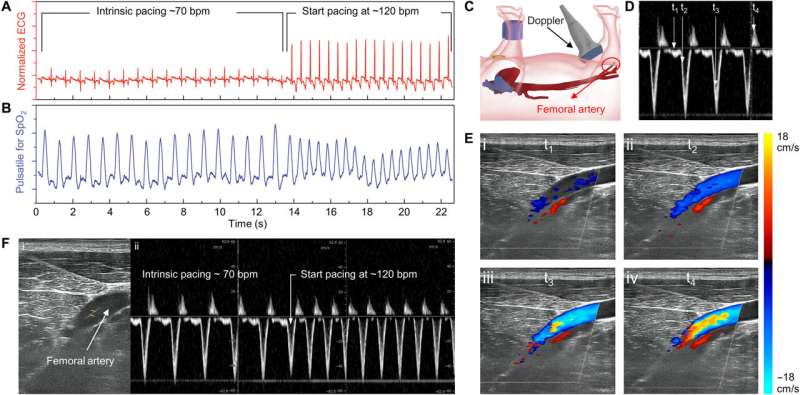
After implanting the device in the anterior cardiac vein, the scientists demonstrated the capacity of the microtubular device to re-energize the non-beating heart, recorded via cardiac electrocardiograms to restore myocardial contraction and perform wireless, and leadless myocardial stimulation.
Designing the self-assembled microtubular pacemaker
The scientists designed the self-assembled microtubular electronics to suit the cardiovascular anatomy and electrophysiology for wireless and battery-free stimulation.
The team illustrated the concept to facilitate intravascular implantation, where the flexible printed circuit board membrane contained a pair of antennas, a rectifier circuit and anode/cathode electrodes to deliver the direct current pulses for myocardial stimulation. The team designed the smaller electrodes to maintain an optimal current density to reduce power consumption during cardiac stimulation. The setup stored the direct current energy before delivering direct current pulses to the anode and cathode electrodes.
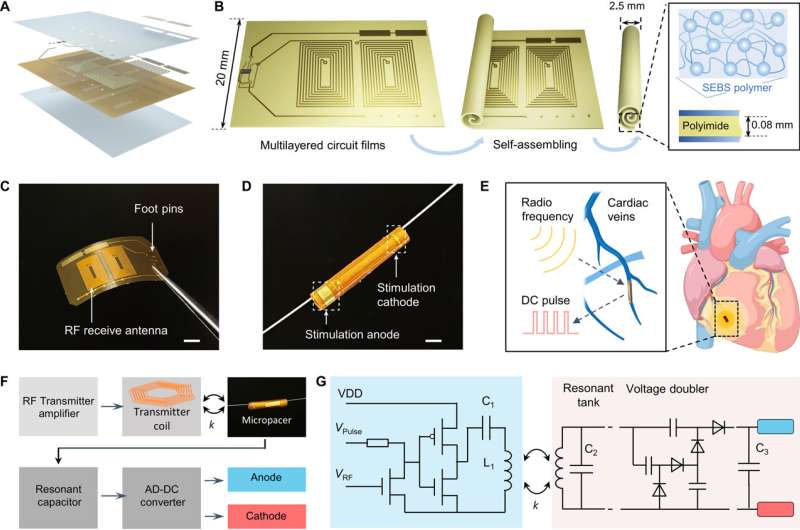
Optimizing the efficiency of the pacemaker through magnetic field stimulation
The scientists optimized the power transfer efficiency through magnetic field stimulation from the transmitter coil to the receiver coil using the ANSYS software. They noted the maximum strength of the magnetic field to occur in the region proximal to the transmitter coil.
Myocardial contraction typically generates a periodic misalignment around the original position during a cardiac cycle. As a result, the alignment of the transmitter and receiver coil influenced the efficiency of inductive powering transferring.
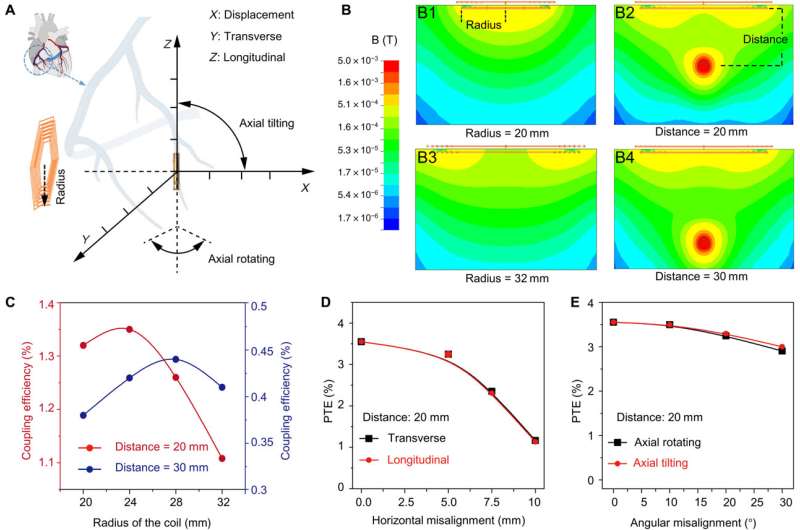
The team studied the strength of the inductively powered system through in vitro testing, where the initiation and termination of radiofrequency pulses were coupled to the direct current pulses. They used a two-circuit architecture to compare radiofrequency alternate current, direct current conversion with a full bridge rectifier, to provide a sufficient energy threshold to re-energize the non-beating heart of a porcine animal model.
Using electrical impedance spectroscopy, Wang and colleagues studied the electrical impedance and phase of the stimulating electrodes.
Outlook: Biocompatibility of the microtubular electronics
The team tested the biocompatibility of the materials by using an in vitro incubation assay and included peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to investigate the surface-biocompatibility and inflammatory response of a variety of materials. The constituent population of PBMCs included granulocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes that actively triggered inflammation and an immune response upon exposure to a biomaterial.
When the bioengineers incubated the blood cells with materials used in the microtubular pacemaker, they noted the absence of cell toxicity and immune responses for up to a week. The constructs showed hemocompatibility and immunogenicity in the microtubular pacemaker.
In this way, the scientists further explored intravascular pacing to restore electromechanical coupling and blood circulation. The porcine heart models resembled human physiology suited for clinical translational in vivo studies.
The team recorded myocardial contraction relative to electrical stimulation as epicardial movements.
The self-assembled microtubular pacemaker provided an innovative method for intravascular deployment with translational impact in cardiac, gastric, and urological stimulations; eliminating the need for a charge storage unit in bioelectronics, with suitability for open-chest thoracotomy and to accelerate wound healing post-implantation.
More information:
Shaolei Wang et al, A self-assembled implantable microtubular pacemaker for wireless cardiac electrotherapy, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adj0540
Journal information:
Science Advances
Source: Read Full Article